A Dive into Health Apps: Types, Trends & Tips for Success

Innovative mobile health apps are transforming the healthcare industry, providing opportunities to improve access to care, quality of care, clinical outcomes and reduce costs.
Types of Health Apps
Mobile health apps can be divided into two categories: apps for consumers (i.e. patients or the general public) and apps for health professionals.
For a more in depth look at some of the health apps listed below, take a look at our blog post: Modernising Healthcare, One App at a Time.
Health Apps for Consumers
New mobile experiences are evolving consumer expectations and the notion of care anytime, anywhere.
More and more consumers are now embracing mobile health apps to enable them to communicate with providers, display test results and health summaries, list medications, facilitate prescription refills, schedule appointments and to record their own patient-generated health data.
Types of health apps for consumers:
- Education & Prevention
- Scheduling & Reminders
- Patient Engagement & Support
- Chronic Disease Management
- Condition Education & Management
- Telehealth & Telemedicine
- Prescription Filling & Adherence
- Health Services Directory
- Self-Monitoring
- Symptom Checkers
- Rehabilitation Programs
- Lifestyle & Wellness
- Mental Health
- Fitness & Dieting
- Women’s Health
Health Apps for Professionals
The adoption of mobile apps by healthcare professionals provides an opportunity to streamline workflows, increase efficiency and improve the quality of care.
Types of health apps for professionals:
- Medical Reference & Database
- Drug Reference
- Disease Diagnosis
- Medical Calculators
- Clinical Communication
- Hospital Information Systems (i.e. health records)
- Medical Education & Teaching
- Telehealth
- Patient Health Tracking
- Remote Patient Monitoring
- Appointments & Clinical Assistance
- Managing Clinical & Financial Records
- Professional Networking
‘Real World’ Use Cases
According to Research2Guidance, the most popular use cases for mobile health apps are “Connection to doctors”, followed by “Diabetes”, “Heart, circulation, blood” and “Medication”.
Here are just a few use cases from the health apps built on the Liquid State platform:
- [Women’s Health] Healthy Pregnancy App: This app supports women through their pregnancy journey, incorporating interactive measurement tools (i.e. due date calculator, contraction timer) and an in-app content library that is personalised based on the stage of pregnancy.
- [Patient Engagement & Support] Children’s Hospital App: This app supports children and caregivers during their hospital journey, providing important hospital and procedural information.
- [Patient Engagement & Support] Patient Journey Tracker: This app provides patients with personalised information related to their specific healthcare journey whilst also allowing caregivers to track a patients progress through day surgery.
- [Medical Reference & Database] Medical Handbook: This app provides clinicians access to industry standard pathology handbooks, with searchable and indexed content for easy reference.
What’s Trending?
The global mHealth (mobile health) app market is expected to reach up to US$102.35 billion by 2023, with the increased adoption of smartphones and the continued heavy investment into the digital health market being the key driving factors fuelling growth.
It is estimated that over 200 health apps worldwide are being added each day to the top app stores, with over 318,000 health apps available in 2017 alone (IQVIA). Despite the fast growth of this market, there is already evidence of health apps playing a positive role in both patient outcomes and the costs of care.
According to an Ernst & Young survey, both patients and physicians are ready for increased digital engagement. Approximately 85% of health apps in the market today are for wellness, designed to be used primarily by the consumer, and the remaining 15% are medical, designed to be used by physicians (Business Insider).
Related Why Healthcare Needs Digital Health Apps
The Healthcare Consumer
Healthcare consumers continue to show strong use of digital technology, with numbers rising each year. In fact, the adoption of digital health technology is at its highest rate ever – with 89% of respondents using at least one digital health tool in 2018 (Rock Health).
According to Accenture , 75% of consumers said technology is important to managing their health, with 48% using mobile health apps. A 2015 survey found that 58% of mobile users have already downloaded at least one mobile health app and 41% have downloaded more than five. More importantly, 79% of consumers are more likely to select a provider who allows them to conduct healthcare interactions online or on a mobile device and 50% of consumers said they would leave their current providers for one that promises better technology.
The mHealth Economic 2017 study found that the top 3 fields with the best market potential for mhealth solutions were Diabetes, followed by Obesity and Depression.
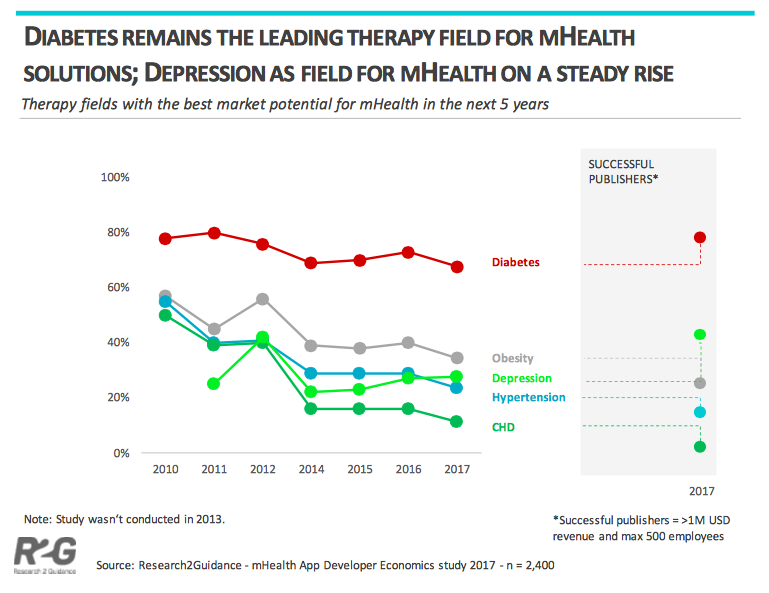
Health apps have already proven reductions in acute care utilisation across 5 patient populations: diabetes prevention, diabetes care, asthma, cardiac rehabilitation and pulmonary rehabilitation. It is estimated that the use of apps in these 5 patient populations could save the U.S. healthcare system $7 billion per year; driven by the reduction of hospital admissions and emergency department visits (IQVIA).
Related Engaging the Healthcare Consumer: The Key to Success in 2019
The Health Professional
Two-thirds of health IT executives indicate that the use of mobile technology will substantially or dramatically impact the delivery of healthcare in the future (HIMSS). In fact, 80% of physicians already prefer to use smartphones and medical apps during their practice.
“The use of smartphones will soon be ubiquitous in clinical environments. This technology offers the potential to improve clinical communications, enhance learning, and improve patient care.”
– Angarita et al.
According to HIMSS, the percent of clinicians using apps to actively engage in direct patient care has grown in the past year in several key areas, including:
- Collection of data at the bedside (45%)
- Use of bar code reader on mobile devices (38%)
- Monitoring data from medical devices (34%)
- Capture visual representation of patient data (27%)
Mosa et al. found that the most useful apps for health professionals and medical students were drug reference apps, digital medical textbooks, references for disease diagnosis, and medical calculator apps.
Tips for Success
Before diving into some tips for success, it is important to highlight the most common reasons why health apps fail:
- The app had poor design and usability,
- There was a lack of involvement and input from key stakeholders (i.e. clinicians and patients) during development,
- The app idea wasn’t properly tested and validated,
- The app was trying to solve too many problems, or
- The understanding of the users and their environment was limited.
Implementing fit-for-purpose solutions that are easy to use, convenient, reliable, scalable and cost-effective is key. To help guide development, here are some shared characteristics of the current top-rated health apps:
- The apps are available in both the App Store and Google Play,
- They are not publicly available to patients – instead require a healthcare organisation to contract a software developer for app development, and
- They satisfy at least 1 of the 3 digital health capabilities that consumers want the most: digital access to medical records, appointment management, and/or prescription refills (Accenture).
For success, it is essential that a health app provides an intuitive user experience, is secure and compliant, and includes some of these common health app features:
- A content library
- Tracking tools & analytics
- Appointments & reminders
- Notifications & messaging
- Access to records
Related: 4 Best Practices for Developing mHealth Apps
With the right health apps, your organisation will be able to enhance its clinical efficiency whilst improving the quality of care and patient outcomes.
If you have an app idea, contact us today to see how Liquid State can help bring your innovative health solution to life.

